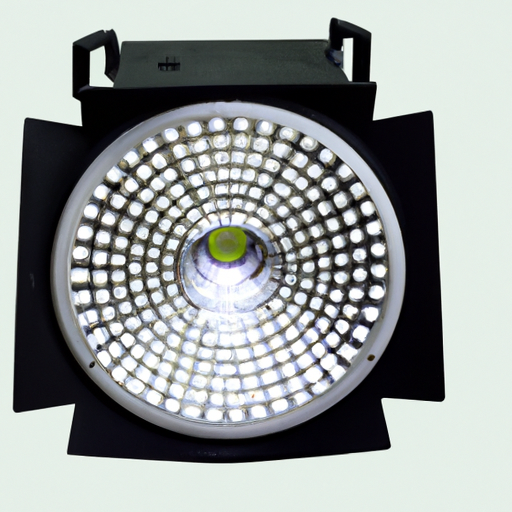
What is the Working Principle of LED Floodlight Spot Inventory?
I. Introduction
A. Definition of LED Floodlights
LED floodlights are powerful lighting fixtures that utilize Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) to produce bright, focused illumination. Unlike traditional incandescent or halogen floodlights, LED floodlights are designed to provide high-intensity light while consuming significantly less energy. They are commonly used in various settings, including outdoor spaces, commercial buildings, and industrial environments.
B. Importance of LED Floodlights in Various Applications
The versatility and efficiency of LED floodlights make them an essential component in modern lighting solutions. They are widely used for outdoor lighting in sports fields, parking lots, and building exteriors, as well as for indoor applications in warehouses and retail spaces. Their ability to enhance visibility and safety has made them a popular choice for security lighting as well.
C. Purpose of the Article
This article aims to explore the working principle of LED floodlights, delving into the technology behind them, their components, and their applications. By understanding how LED floodlights operate, readers can appreciate their advantages and make informed decisions when selecting lighting solutions for their needs.
II. Understanding LED Technology
A. What is an LED?
1. Definition and Composition
A Light Emitting Diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. LEDs are composed of a chip made from a combination of materials, typically gallium, arsenic, and phosphorus, which create a p-n junction. This junction is crucial for the light-emitting process.
2. How LEDs Work
When electricity flows through the LED, electrons move from the n-type layer (negative) to the p-type layer (positive). As these electrons recombine with holes in the p-type layer, they release energy in the form of photons, which is visible light. The color of the emitted light depends on the materials used in the semiconductor.
B. Advantages of LED Technology
1. Energy Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of LED technology is its energy efficiency. LEDs consume up to 80% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs, making them a cost-effective lighting solution.
2. Longevity
LEDs have a much longer lifespan compared to conventional lighting options. While incandescent bulbs may last around 1,000 hours, LED floodlights can last up to 50,000 hours or more, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
3. Low Heat Emission
LEDs generate very little heat compared to traditional lighting sources. This characteristic not only enhances safety but also contributes to energy savings, as less energy is wasted as heat.
4. Environmental Impact
LEDs are more environmentally friendly than traditional lighting options. They contain no toxic materials like mercury and are fully recyclable, reducing their overall environmental footprint.
III. Components of LED Floodlights
A. LED Chips
1. Types of LED Chips
LED floodlights utilize various types of LED chips, including SMD (Surface Mount Device) and COB (Chip on Board) technologies. SMD LEDs are known for their compact size and versatility, while COB LEDs provide higher lumen output and better thermal management.
2. Role in Light Emission
The LED chips are the heart of the floodlight, responsible for converting electrical energy into light. The quality and type of LED chip used directly impact the brightness and efficiency of the floodlight.
B. Housing and Lens
1. Materials Used
The housing of LED floodlights is typically made from durable materials such as aluminum or polycarbonate, designed to withstand harsh weather conditions. The lens, often made from tempered glass or polycarbonate, protects the LED chips while allowing maximum light transmission.
2. Importance of Design for Light Distribution
The design of the housing and lens is crucial for effective light distribution. A well-designed lens can help focus the light beam and reduce glare, ensuring that the illumination is directed where it is needed most.
C. Power Supply
1. Function of the Driver
The power supply, or driver, is an essential component of LED floodlights. It converts the incoming AC (alternating current) from the electrical grid into DC (direct current) suitable for the LED chips. The driver also regulates the current and voltage to ensure optimal performance.
2. Voltage and Current Regulation
Proper voltage and current regulation are vital for the longevity and efficiency of LED floodlights. A high-quality driver prevents fluctuations that could damage the LED chips and ensures consistent light output.
D. Heat Sink
1. Importance of Thermal Management
Heat management is critical in LED technology. Excessive heat can reduce the efficiency and lifespan of LED chips. A heat sink dissipates heat away from the LED chips, maintaining optimal operating temperatures.
2. Materials and Design Considerations
Heat sinks are typically made from materials with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum. The design of the heat sink, including its size and surface area, plays a significant role in its effectiveness in managing heat.
IV. Working Principle of LED Floodlights
A. Light Generation Process
1. Electron Movement in LED Chips
The light generation process begins with the movement of electrons within the LED chips. When an electric current is applied, electrons flow from the n-type layer to the p-type layer, where they recombine with holes.
2. Photon Emission
As electrons recombine with holes, they release energy in the form of photons. This process is known as electroluminescence, and it is the fundamental mechanism behind the light emitted by LEDs.
B. Light Distribution
1. Role of Reflectors and Lenses
To maximize the effectiveness of LED floodlights, reflectors and lenses are used to control the direction and spread of light. Reflectors help direct the light output, while lenses can modify the beam angle to achieve the desired coverage.
2. Beam Angle and Coverage
The beam angle of an LED floodlight determines how wide or narrow the light distribution will be. A narrow beam angle is ideal for focused lighting, while a wider beam angle is suitable for illuminating larger areas.
C. Power Management
1. Conversion of AC to DC
The power management system in LED floodlights ensures that the incoming AC power is converted to DC power, which is necessary for the operation of the LED chips. This conversion is typically handled by the driver.
2. Dimming and Control Options
Many LED floodlights come with dimming and control options, allowing users to adjust the brightness according to their needs. This feature enhances energy efficiency and provides flexibility in lighting design.
V. Applications of LED Floodlights
A. Outdoor Lighting
1. Sports Fields
LED floodlights are commonly used in sports fields to provide bright, uniform lighting for games and events. Their energy efficiency and long lifespan make them an ideal choice for outdoor sports facilities.
2. Parking Lots
In parking lots, LED floodlights enhance safety and security by illuminating dark areas. Their ability to provide bright light while consuming less energy makes them a cost-effective solution for commercial properties.
3. Building Exteriors
LED floodlights are often used to highlight building exteriors, enhancing aesthetics and security. They can be strategically placed to illuminate architectural features and provide visibility at night.
B. Indoor Lighting
1. Warehouses
In warehouses, LED floodlights provide bright, even lighting that improves visibility for workers and enhances safety. Their long lifespan reduces maintenance costs associated with frequent bulb replacements.
2. Retail Spaces
Retail spaces benefit from LED floodlights as they create an inviting atmosphere for customers. The ability to adjust brightness levels allows retailers to create different moods and highlight specific products.
C. Security and Safety
1. Surveillance Areas
LED floodlights are essential for surveillance areas, providing bright illumination that deters criminal activity. Their energy efficiency ensures that security lighting can be maintained without incurring high costs.
2. Emergency Lighting
In emergency situations, LED floodlights can provide critical illumination for evacuation routes and safety zones. Their reliability and quick response times make them a vital component of emergency lighting systems.
VI. Advantages of Using LED Floodlights
A. Cost-Effectiveness
1. Initial Investment vs. Long-Term Savings
While the initial cost of LED floodlights may be higher than traditional lighting options, the long-term savings in energy costs and maintenance make them a cost-effective choice. Their longevity means fewer replacements and lower overall expenses.
B. Versatility
1. Different Sizes and Designs
LED floodlights come in various sizes and designs, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Whether for residential, commercial, or industrial use, there is an LED floodlight to meet specific lighting needs.
C. Environmental Benefits
1. Reduced Carbon Footprint
By consuming less energy and having a longer lifespan, LED floodlights contribute to a reduced carbon footprint. This makes them an environmentally friendly choice for lighting solutions.
2. Recyclability of Components
Many components of LED floodlights are recyclable, further minimizing their environmental impact. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in modern lighting design.
VII. Challenges and Considerations
A. Initial Cost vs. Long-Term Benefits
While LED floodlights offer significant long-term savings, the initial investment can be a barrier for some consumers. It is essential to weigh the upfront costs against the potential savings over time.
B. Quality Variations in the Market
Not all LED floodlights are created equal. Variations in quality can affect performance, longevity, and energy efficiency. Consumers should research and choose reputable brands to ensure they are getting a reliable product.
C. Importance of Proper Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for maximizing the performance of LED floodlights. Ensuring that fixtures are installed correctly and maintained regularly can prevent issues and extend their lifespan.
VIII. Conclusion
A. Summary of Key Points
LED floodlights represent a significant advancement in lighting technology, offering energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility. Understanding their working principles, components, and applications can help consumers make informed decisions.
B. Future Trends in LED Floodlight Technology
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in LED floodlight design, including improved energy efficiency, smart lighting features, and enhanced control options.
C. Final Thoughts on the Importance of LED Floodlights in Modern Lighting Solutions
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability and energy efficiency, LED floodlights play a vital role in modern lighting solutions. Their ability to provide bright, reliable illumination while minimizing environmental impact makes them an essential choice for various applications.
IX. References
A. Academic Journals
- Journal of Light & Visual Environment
- IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications
B. Industry Reports
- LED Lighting Market Analysis Report
- Energy Efficiency in Lighting: A Comprehensive Review
C. Manufacturer Specifications and Guidelines
- Philips Lighting: LED Floodlight Specifications
- Cree Lighting: LED Technology Overview
This comprehensive exploration of LED floodlights highlights their working principles, advantages, and applications, providing valuable insights for anyone considering these innovative lighting solutions.